异常处理
- 处理异常
- 抛出异常-让调用方去处理异常
- 格式 在方法名处,添加"throws 异常类型1,异常类型2...."
- 特定位置抛出异常, 类似python中的raise; 此处抛出的"运行时异常"不需要在方法名处添加异常类型,但"编译异常"需要添加
- 抛出格式 throw new Excetption("xxxx")
java// 处理异常 public class ErrorTest{ public String[] names = new String[]{"tom", "jerry"}; public static void main(String[] args) { ErrorTest e1 = new ErrorTest(); try { System.out.println(e1.names[10]); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println(e); }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); }finally{ System.out.println("finally"); } } }java// 抛出异常 class Dog{ public void div(int x) throws Exception{ if (x == 0){ // 向上抛出异常 throw new Exception("数字不能为0"); } System.out.println(100/x); } } public class ErrorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog g = new Dog(); try { g.div(0); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }Java多线程
- 继承thread类
- 实现Runable接口 实现run方法
- 实现Callable接口 实现call方法
继承thread类
javaclass App extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("get url"); } } public class threadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { App app = new App(); app.start(); } }实现Runable接口
javaclass App implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("this is :" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class threadTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { App app = new App(); new Thread(app).start(); System.out.println("main thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }实现Callable接口
javaimport java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; class AppCall implements Callable { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) { Thread.sleep(100); sum += i; } return sum; } } public class threadTest06 { public static void main(String[] args) { AppCall app = new AppCall(); FutureTask ftask = new FutureTask(app); Thread t = new Thread(ftask); t.start(); try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("main over"); try { System.out.println("thread result:" + ftask.get()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }线程中常用方法
- join 直到当前线程执行完毕,主线程处于阻塞
- yield 让CPU让出当前线程的执行
- getPriority 获取当前线程的执行优先级
- setPriority 设置当前线程的执行优先级【1-10之间】
线程的生命周期
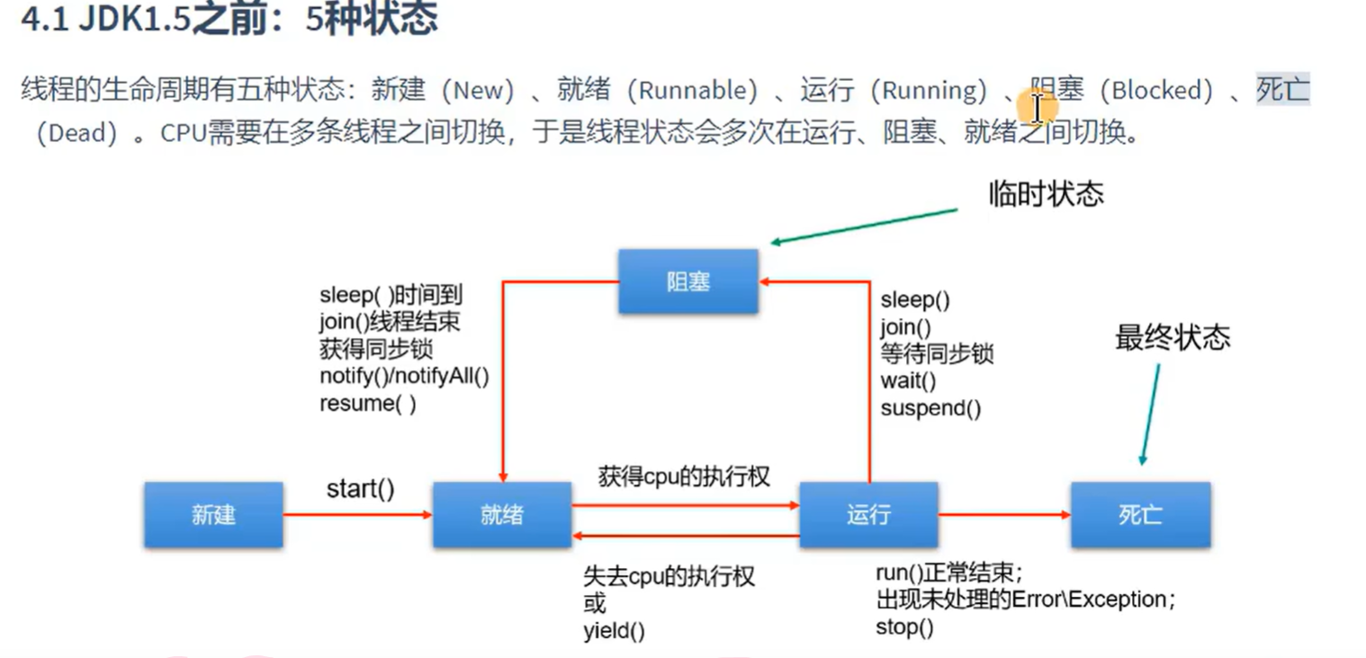
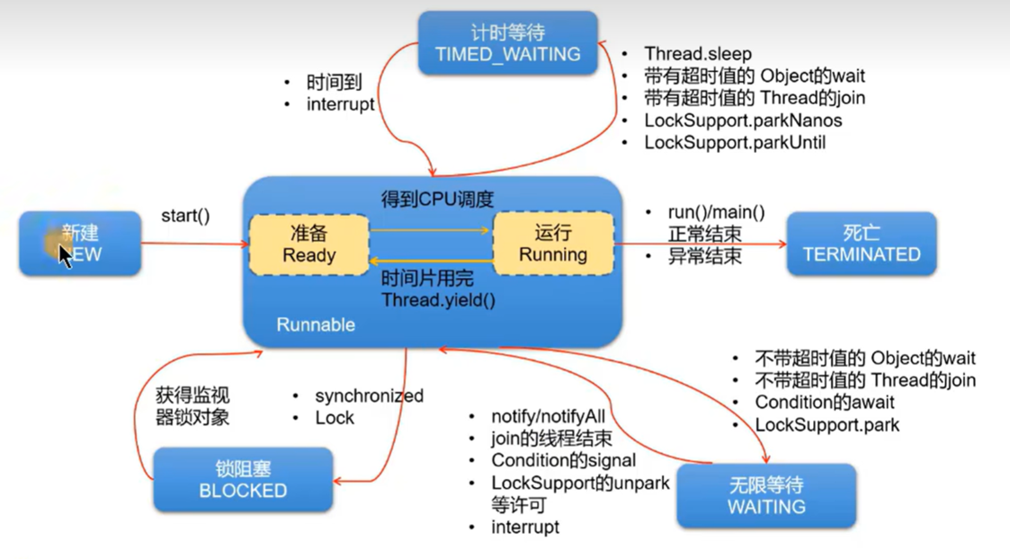
线程的同步(使用
synchronized进行资源同步)- 使用synchronized代码块
java// 监视器必须唯一 // 实现Runable接口,监视器可以使用 this 或者 类名.class // 继承thread类,监视器可以使用 类名.class 慎用 this synchronized(监视器){ // 代码块 }- 使用synchronized方法
java// 监视器必须唯一 监视器默认是this // 实现Runable接口,自动是唯一的 // 继承thread类,非静态的方法,监视器还是this,不唯一 // 静态方法,监视器是当前类,唯一,可以使用 public synchronized void incr (){ // 代码块 }javapublic class threadTest04 implements Runnable { private int ticket = 10; // 出现线程数据异常问题 // @Override // public void run() { // ticket--; // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "当前剩余数量:" + ticket); // } // 在【属性】和方法上面加 synchronized 同步来限制资源的访问。被 synchronized 包围的代码块称为同步代码块。 @Override public void run() { synchronized (this) { ticket--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "当前剩余数量:" + ticket); } } // 在属性和【方法】上面加 synchronized 同步来限制资源的访问。 // @Override // public synchronized void run() { // ticket--; // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "当前剩余数量:" + ticket); // } public static void main(String[] args) { threadTest04 th = new threadTest04(); new Thread(th).start(); new Thread(th).start(); new Thread(th).start(); new Thread(th).start(); new Thread(th).start(); new Thread(th).start(); } }String常用方法
String->char[] 使用toCharArray()
String->byte[] 使用getBytes()
常见类库
StringBuffer 当前类库将创建一个引用类型的字符串,可以对字符串进行修改操作,由于包含
synchronized,线程安全StringBuilder 当前类库将创建一个引用类型的字符串,可以对字符串进行修改操作,非线程安全
Date 获取时间类
SimpleDateFormat时间格式化类
Calender类
LocalDate类
LocalTime类
LocalDateTime类
Math类
Random类
BigDecimal类 高精度数据计算时使用
Timer类
TimeTask类
// Date and SimpleDateFormat simple code
javaimport java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class datedemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Date d = new Date(); System.out.println(d.toString()); System.out.println(d.getTime()); java.sql.Date d2 = new java.sql.Date(1683468299278L); System.out.println(d2.toString()); SimpleDateFormat s = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); // date -> str String ret = s.format(new Date()); System.out.println(ret); // str -> date try { Date d3 = s.parse(ret); System.out.println(d3.toString()); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }// Calender simple code
javapackage chapter07.date01; import java.util.Calendar; public class calenderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); System.out.println(c.getTime()); // 通过get方法 获取当前日期对象在今天的小时 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)); } }// LocalDate and LocalTime and LocalDateTime simple code
javaimport java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.LocalTime; public class jdk8timeDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDate nDate = LocalDate.now(); System.out.println(nDate); System.out.println(nDate.getMonth()); LocalTime nTime = LocalTime.now(); System.out.println(nTime); LocalDateTime nDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(nDateTime); } }集合框架
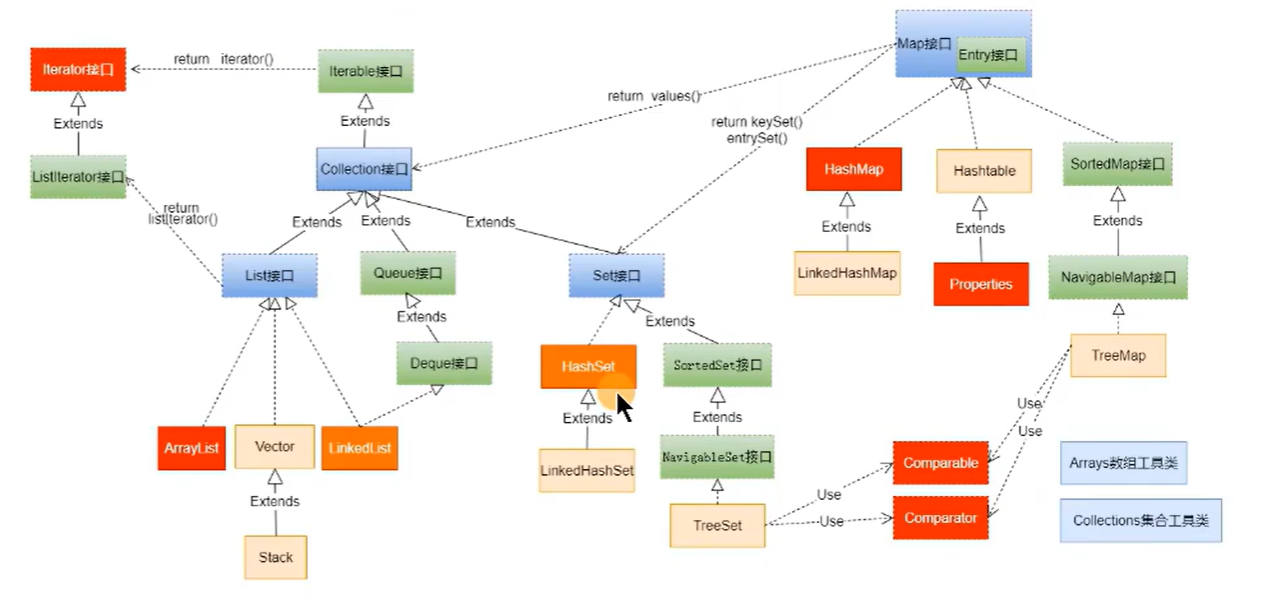
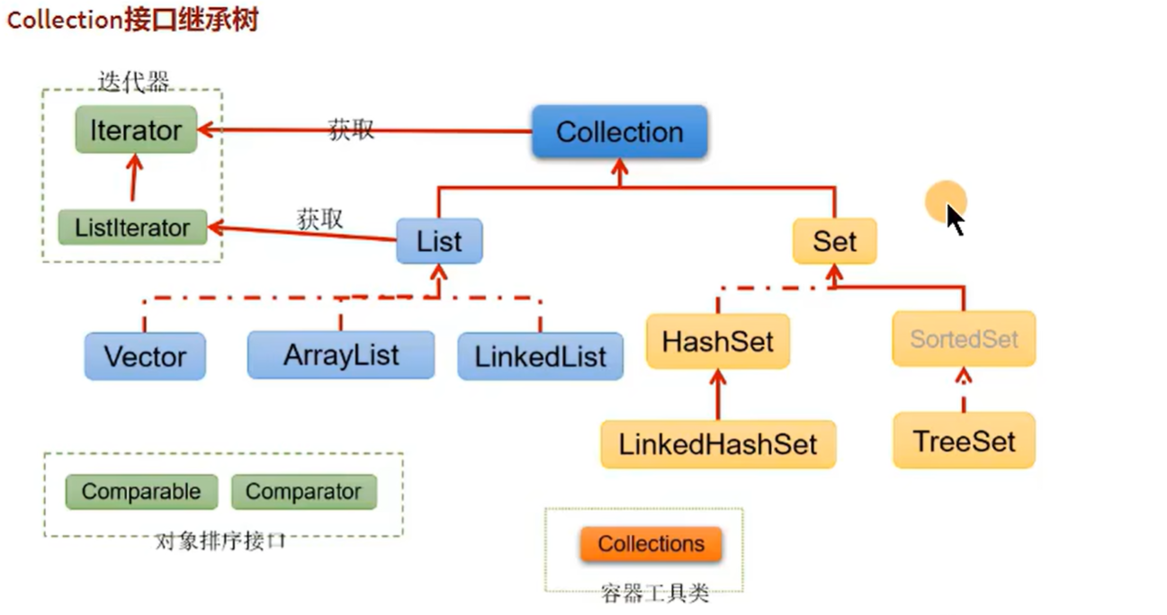
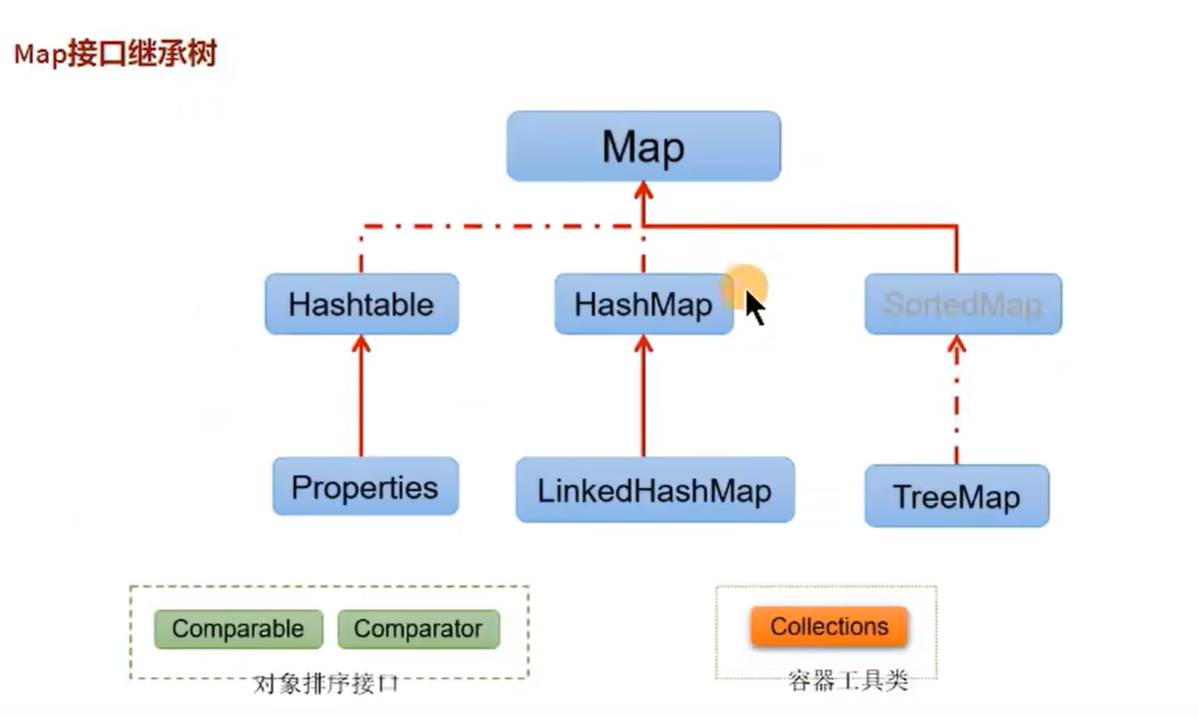 java
javajava.util.Collection // 存一个一个的数据 List: ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector Set: HashSet、LinkedSet、TreeSet java.util.Map // 存一对一对的数据 HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties泛型
markdown# 泛型类语法 [访问权限] class 类名称<范型标识符 1,泛型标识符 2,... ,泛型标识符n>{ [访问权限] 泛型类型标识符 变量名称; [访问权限] 泛型类型标识符 方法名称(){}; [访问权限] 返回值类型声明 方法名称(泛型类型标识 变量名称){}; } # Java泛型对象声明语法 类名称<具体类> 对象名称 = new 类名称<具体类>(); # Java泛型接口 [访问权限] interface 接口名称<泛型标识>{ } # Java泛型方法 【在一般类中定义】 [访问权限]<泛型标识> 泛型标识 方法名称(泛型标识 参数名称){ //do something }javapackage generics; interface AObj<T> { public T getValue(); } // 泛型接口实现方式一 在类上使用泛型 class A1<T> implements AObj<T> { @Override public T getValue() { System.out.println("嗨,你好啊,我是第一种实现方式"); return null; } } // 泛型接口实现方式二 指明具体类型 class A2 implements AObj<String> { @Override public String getValue() { System.out.println("嗨,你好啊,我是第二种实现方式"); return "嗨,你好啊,我是第二种实现方式"; } } public class generics04 { public static void main(String[] args) { A1<String> a = new A1<>(); a.getValue(); A2 b = new A2(); b.getValue(); } }javapackage generics; // 在一般类中定义泛型方法 public class generics05 { public <T> T show(T msg){ System.out.println(msg); return msg; } public static void main(String[] args) { generics05 a = new generics05(); a.show("hello Java generics"); } }File类&IO流
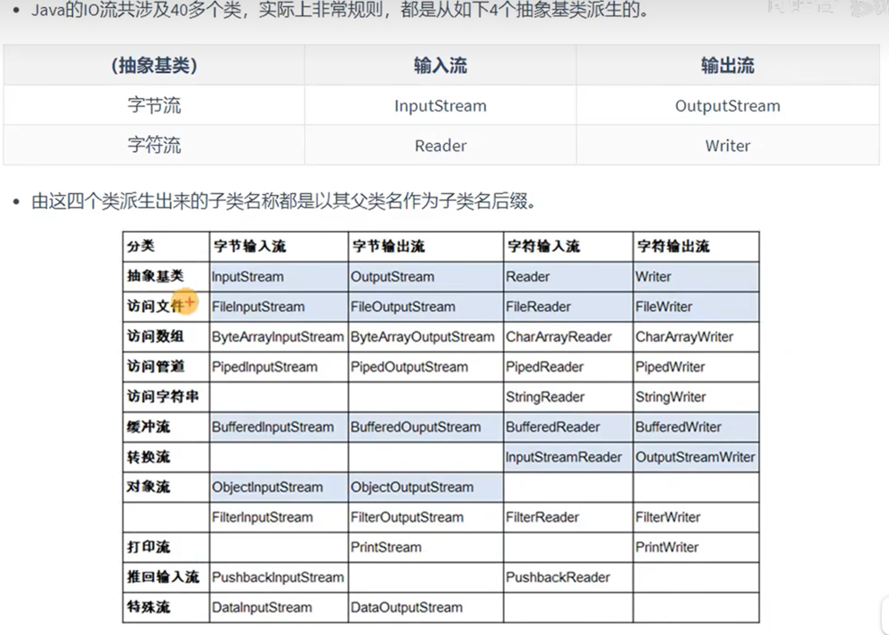
数据流向不同分类
- 输入流(读取到内存中的流)
- 以InputStream、Reader结尾
- 输出流(从内存中写入到其他设备的流)
- 以OutputStream、Writer结尾
- 输入流(读取到内存中的流)
操作数据单位分类
- 字节流(以字节为单位)
- 以InputStream、OutputStream结尾
- 字符流(以字符为单位)
- 以Reader、Writer结尾
- 字节流(以字节为单位)
code 范例
java// 字符输入输出流实现文件内容拷贝 package chapter09; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class file004 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileReader r = new FileReader("./chapter09_file01.txt"); FileWriter w = new FileWriter("./chapter09_file02.txt"); char[] data = new char[2]; int len; while (true) { len = r.read(data); if (len == -1) { break; } w.write(data); } r.close(); w.close(); } }java// 字节输入输出流实现文件内容的拷贝 package chapter09; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class file005 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream r = new FileInputStream("./chapter09_file01.png"); FileOutputStream w = new FileOutputStream("./chapter09_file02.png"); byte[] data = new byte[2]; int len; while (true) { len = r.read(data); if (len == -1) { break; } w.write(data); } r.close(); w.close(); } }java//带缓存的字节输入输出流实现文件内容的拷贝 package chapter09; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class file006 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedInputStream r = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./chapter09_file01.png")); BufferedOutputStream w = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./chapter09_file03.png")); byte[] data = new byte[2]; int len; while (true) { len = r.read(data); if (len == -1) { break; } w.write(data); } r.close(); w.close(); } }
网络编程
code 范例
java// simple tcp server package chapter10; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; public class socket001 { public static void ReadChar(Socket sock) throws IOException { BufferedReader inp = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream(), "GBK")); int size = 20; int len = 0; int lineSize; char[] data = new char[size]; StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder(); while (true) { lineSize = 0; while ((len = inp.read(data)) != -1) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { b.append(data[i]); data[i] = ' '; } lineSize += len; if (len < size) { break; } } System.out.println(b.toString()); b.delete(0, lineSize); } } public static void PutChar(Socket sock) throws IOException, InterruptedException { BufferedWriter outp = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream())); while (true) { outp.write("ping " + (int) (Math.random() * 100)); outp.flush(); Thread.sleep(1000); } } public static void HanderSock(Socket sock) throws IOException { try { System.out.println("start conn..."); new Thread(() -> { try { ReadChar(sock); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); new Thread(() -> { try { PutChar(sock); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); sock.close(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { try (ServerSocket s = new ServerSocket(8081)) { while (true) { Socket sock = s.accept(); new Thread(() -> { try { HanderSock(sock); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }java// simple tcp client package chapter10; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class socket002 { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException { Socket sock = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8081); BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream())); char[] data = new char[20]; StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder(); int len; while ((len = bf.read(data)) != -1) { b.append(data, 0, len); System.out.println(b.toString()); b.delete(0, len); } bf.close(); sock.close(); } }